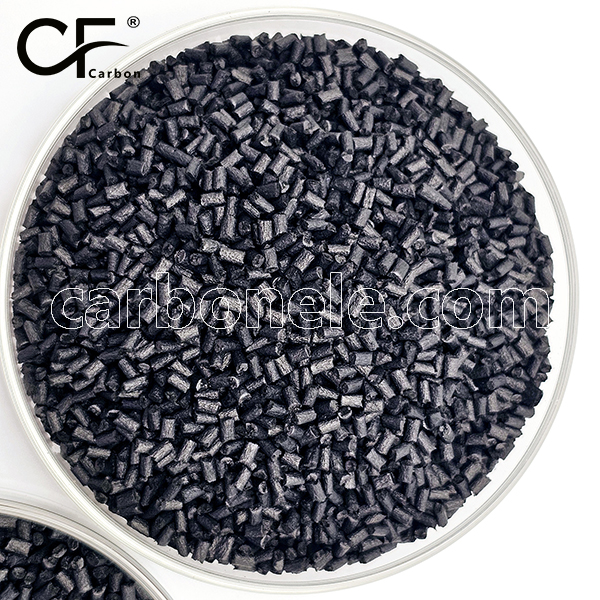
Stable PPA-CF20 Material-Perfect for Pumps
PPA-CF20 carbon fiber reinforced plastic—heat-resistant, rigid engineering material for pumps/auto parts. Lightweight metal alternative with superior dimensional stability & chemical resistance
- Manufacturer: Carbon New Material
- OEM/ODM: Acceptable
- Color: Black
- Free samples: ≤10kg
- MOQ: 100kg
- Port: Xiamen
- Model number: PPA-CF-BCA2
- Matrix Resin: PPA
- Reinforcing Filler: Carbon fiber
- Appearance: Granules
- Grade: Injection/extrusion grade
- Packaging: 25kgs/bag
Introduction to PPA-CF20
When industries search for advanced thermoplastic solutions that combine stability, strength, and design flexibility, PPA-CF20 consistently stands out. This innovative composite is engineered from polyphthalamide reinforced with carbon fiber, offering a balance of rigidity, heat resistance, and long-term reliability.
Companies across automotive, industrial, and consumer goods sectors increasingly turn to PPA-CF20 to replace metals and lower-performance plastics. From small functional components to complex mechanical assemblies, this material delivers consistent results that push the boundaries of performance.
Why Choose PPA-CF20
PPA-CF20 offers a distinct combination of properties that make it superior to many alternatives. It resists deformation, maintains stability under stress, and provides an excellent surface finish suitable for high-precision components.
The carbon fiber reinforcement ensures long-term dimensional stability, making it particularly valuable where consistency is critical. In addition, PPA-CF20 simplifies manufacturing through injection molding, allowing cost-effective production of intricate designs while retaining premium strength.
PPA-CF20 in Pump Applications
One of the most compelling examples of PPA-CF20 in use is within pump components. Pumps require materials that withstand constant mechanical stress, exposure to fluids, and temperature variations. Traditional plastics may warp or degrade over time, and metals can be costly or prone to corrosion.
PPA-CF20 offers a balance: lightweight yet highly resistant, precise yet durable. When used in pump housings or impellers, the material enhances performance by providing stability and reducing wear. Engineers benefit from its ability to retain shape even after long operational cycles, ensuring pumps deliver consistent flow and reliability.
Stability for Precision Flow
In pumps, stability is everything. PPA-CF20 maintains dimensional accuracy, ensuring tight tolerances are preserved during operation. This guarantees that fluid movement remains precise without leakage or performance loss.
Whether for industrial water pumps, chemical circulation units, or compact home appliances, the material’s strength supports both efficiency and longevity.
Durability Against Stress
Pumps face repeated cycles of pressure and motion. PPA-CF20 absorbs these challenges by maintaining high mechanical strength. Unlike brittle plastics, it does not crack under stress. Unlike metals, it does not corrode in damp or chemically aggressive environments.
This resilience makes it the preferred option for manufacturers seeking to minimize maintenance and maximize reliability.
Key Advantages of PPA-CF20
Lightweight Yet Strong
The carbon fiber reinforcement in PPA-CF20 gives it exceptional strength-to-weight performance. This allows manufacturers to reduce component weight while maintaining or even enhancing durability. The reduced mass is especially advantageous for moving parts, lowering energy consumption and wear.
Dimensional Stability
Dimensional stability sets PPA-CF20 apart. It resists thermal expansion and moisture absorption, two common causes of failure in standard plastics. This ensures that critical pump parts remain consistent in shape and performance, even under challenging conditions.
Resistance to Chemicals
Industrial environments often involve aggressive fluids. PPA-CF20 resists many chemicals, making it ideal for pumps exposed to oils, fuels, coolants, or cleaning agents. This chemical resistance prolongs the life of components and reduces the risk of costly breakdowns.
Heat Resistance
Where pumps encounter elevated temperatures, PPA-CF20 retains strength. Unlike traditional plastics that soften or deform, it maintains rigidity, ensuring uninterrupted operation. This makes it an excellent choice for applications requiring exposure to hot fluids or high operational heat.
Industrial Applications of PPA-CF20 Beyond Pumps
While pumps demonstrate the material’s capabilities clearly, PPA-CF20 excels in a broad range of applications.
Automotive
In automotive systems, PPA-CF20 is trusted for under-the-hood parts exposed to heat and mechanical loads. Engine covers, brackets, and fluid system components benefit from its stability. By reducing weight and resisting thermal stress, it contributes to fuel efficiency and long service life.
Electrical Components
Electrical housings and connectors rely on the precision and insulation properties of PPA-CF20. Its ability to maintain tight tolerances ensures secure fits, while its resistance to heat prevents deformation during extended use.
Consumer Appliances
Home appliances demand both durability and a refined finish. PPA-CF20 provides manufacturers with a strong yet aesthetic option, particularly in parts subject to heat or repeated stress. Coffee machines, washing devices, and kitchen tools are examples where the material ensures long-term reliability.
Design Flexibility with PPA-CF20
Engineers often face the challenge of balancing design creativity with performance demands. PPA-CF20 opens possibilities by supporting complex geometries through injection molding while still delivering stability.
Designers can reduce assembly complexity by integrating multiple functions into one molded part. The material’s smooth surface finish also improves sealing capabilities, reducing the risk of leaks in pump applications.
Sustainability and PPA-CF20
Sustainability is a growing concern across industries. By using PPA-CF20, manufacturers reduce reliance on metals that require energy-intensive processing. Its lightweight nature also contributes to reduced energy consumption in transportation and mechanical systems.
Additionally, its durability minimizes waste by extending product lifetimes, making it an environmentally conscious material choice.
PPA-CF20 vs Traditional Materials
Compared to Metals
While metals offer strength, they are heavier and prone to corrosion. PPA-CF20 delivers comparable strength at a fraction of the weight and with superior resistance to environmental degradation.
This combination reduces maintenance costs and enhances efficiency.
Compared to Standard Plastics
Conventional plastics may be easier to process but fail under stress, heat, or exposure to chemicals. PPA-CF20 stands out by overcoming these weaknesses, providing high-performance characteristics while still being moldable into complex forms.
Real-World Example: Pump Manufacturing with PPA-CF20
Consider a manufacturer producing pumps for industrial cooling systems. The company previously used metal components that were durable but costly and required protective coatings. After switching to PPA-CF20, the manufacturer reduced production costs while improving pump efficiency.
The lightweight components made assembly easier, and the stability of the material ensured pumps maintained precise flow over long operational cycles. Maintenance intervals decreased, and customer satisfaction improved. This case illustrates how PPA-CF20 translates material science into tangible business advantages.
How PPA-CF20 Enhances Product Value
Manufacturers using PPA-CF20 benefit from more than just performance. The ability to market pumps and components as lightweight, durable, and resistant to harsh environments increases customer trust.
Products made with this material stand out for their reliability, giving brands a competitive edge in demanding markets.
The Future of PPA-CF20 in Industry
As technology advances, PPA-CF20 will continue to gain traction. Industries seek materials that balance performance, cost, and sustainability. With its track record in pumps and beyond, it is positioned as a material of choice for forward-looking manufacturers.
Innovations in processing and design integration will expand its applications further, making it central to the future of advanced manufacturing.
Conclusion
PPA-CF20 represents a modern solution for industries requiring stability, durability, and versatility. From pumps to automotive, from electrical systems to consumer products, it proves its value in diverse environments.
Its ability to replace metals and outperform conventional plastics makes it a cornerstone of innovation. Companies seeking reliable, high-performance components will continue to turn to PPA-CF20 as the foundation of their designs.
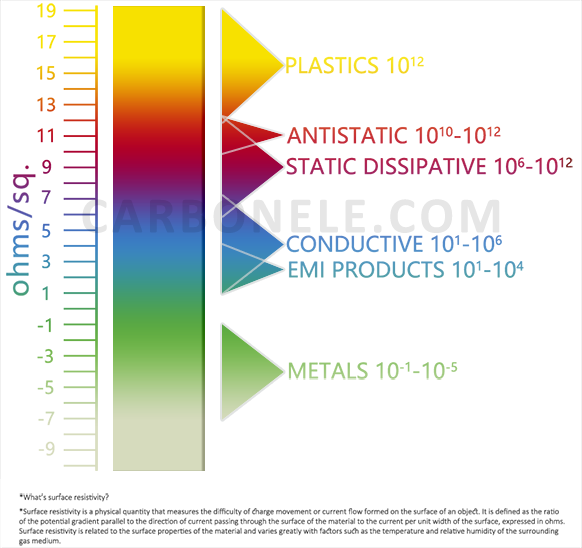
Surface Resistivity Comparison
Conductors < 10⁵ Ω/sq. Antistatic Materials 10⁵ ~ 10¹² Ω/sq. Insulators > 10¹² Ω/sq. Static-Dissipative 10⁶ ~ 10¹¹ Ω/sq. *Key Influencing Factors Humidity: Increased moisture can reduce resistivity (e.g., in polymers). Temperature: Affects carrier mobility (↑ heat may lower semiconductor resistivity). Surface Contamination: Dust/oils alter readings significantly. Additives: Carbon black, metallic fillers can lower resistivity. *Applications Electronics: Antistatic materials (10⁶–10⁹ Ω/sq) prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD). Aerospace: Composites must control resistivity to avoid charge buildup. Medical Devices: Insulating materials (>10¹² Ω/sq) ensure patient safety. *Examples Polypropylene (PP): ~10¹⁶ Ω/sq (excellent insulator). Carbon Fiber Composites: 10³–10⁶ Ω/sq (static dissipation). ESD Flooring: 10⁶–10⁹ Ω/sq.
Get to Know Carbon Fibers
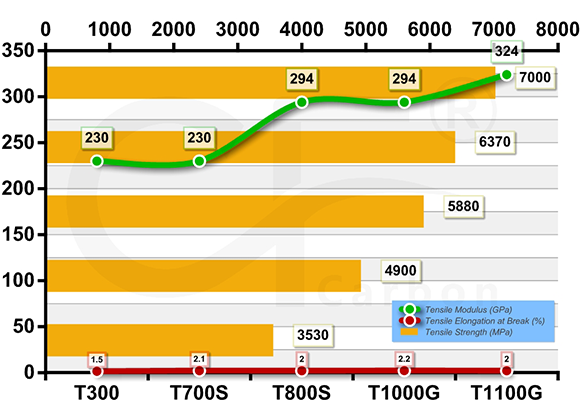
The table presents key performance data of carbon fiber grades. T300, with a tensile strength of 3530 MPa and a tensile modulus of 230 GPa, has a relatively low tensile elongation at break of 1.5% and a body density of 1.76 g/cm³. As the grade increases, for example, T700S shows an enhanced tensile strength of 4900 MPa compared to T300, while maintaining the same tensile modulus but with a higher elongation at break of 2.1%. T800S and T1000G both have a tensile modulus of 294 GPa, and their tensile strengths are 5880 MPa and 6370 MPa respectively. T1100G stands out with the highest tensile strength of 7000 MPa and a tensile modulus of 324 GPa. Generally, with the increase in product grade, the tensile strength and modulus tend to rise, while the density remains relatively stable around 1.8 g/cm³.
How to Buy?
If you want to obtain information such as product specifications, performance, and price, choose a suitable product according to your own needs. Meanwhile, you can ask the manufacturer to provide samples for testing to ensure that the material meets your usage requirements. If you are interested in purchasing this composite material, please contact the manufacturer Carbon (Xiamen) New Material directly.


Frequently Asked Questions
Carbon (Xiamen) New Material Co., Ltd. aims to provide buyers with "one-stop" worry-free high-quality services. Here you can find all information about carbon fiber engineering plastics. If you still have questions, please send us an email for consultation!
-
How can I contact the manufacturer of a product that interests me?
When you find a product you are interested in, you can contact the manufacturer directly by sending an email and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
-
How do I find the products that interest me?
All you need to do is enter the keyword, product name in the search window and press the Enter key on your keyboard. Your search results page will then be displayed. You can also search within the product category pages on the home page. Each category is divided into subcategories, allowing you to refine your search and find products that interest you.
-
Where will I find a buying guide?
Please contact our after-sales service directly and we will provide you with a comprehensive operating guide.
-
What are CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites are materials where carbon fibers are incorporated into a thermoplastic matrix. They combine the strength and stiffness of carbon fibers with the processability and recyclability of thermoplastics. For instance, they are used in automotive parts like bumper beams.
-
What are the benefits of CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites over traditional composites?
The key benefits include faster production cycles, easier recyclability, and better impact resistance. They also offer design flexibility. An example is in the manufacturing of consumer electronics casings where complex shapes can be achieved more easily.
-
How are CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites processed?
Common processing methods include injection molding, extrusion, and compression molding. Injection molding is widely used for mass production. For example, in the production of small components for the medical industry.
-
What industries use CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
They are utilized in aerospace, automotive, medical, and sports equipment industries. In aerospace, they can be found in interior components. In the medical field, they might be used in prosthetics.
-
How does the carbon fiber content affect the properties of the composites?
Higher carbon fiber content generally leads to increased strength and stiffness but may reduce ductility. A moderate content is often balanced for specific applications. For example, a higher content might be preferred in structural parts of a race car.
-
What are the challenges in using CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
Challenges include higher material costs, complex processing equipment requirements, and ensuring uniform fiber dispersion. Issues with adhesion between the fibers and the matrix can also arise. An example is in achieving consistent quality in large-scale production.