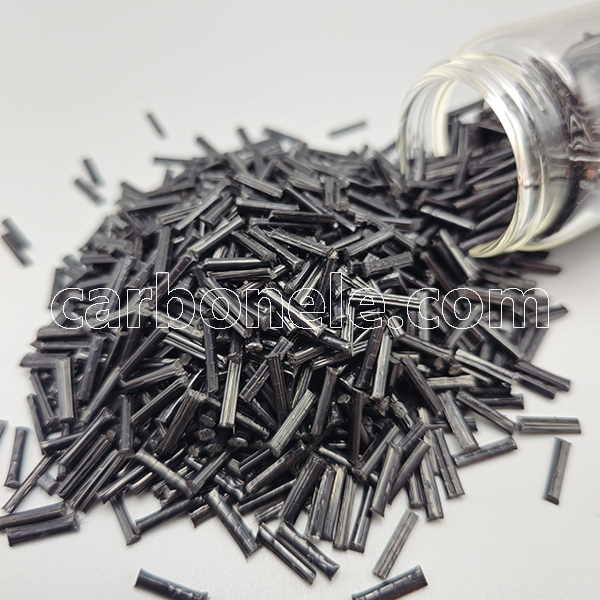
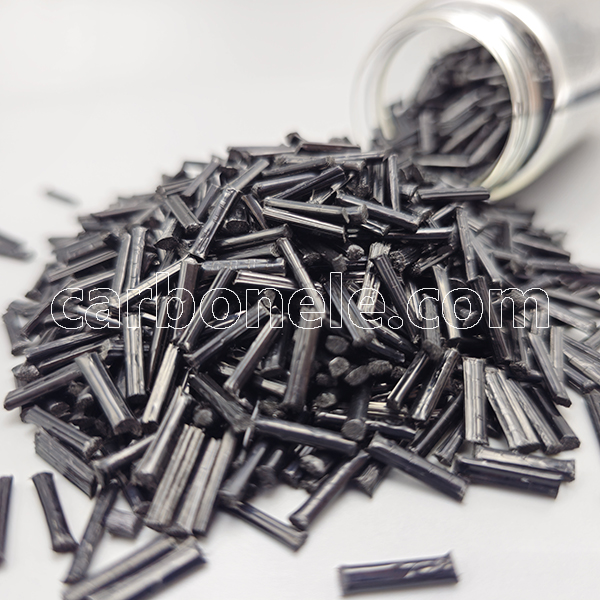
TPU-LCF30 Composite Materials with High Strength and Rigidity
TPU-LCF30 is a high performance thermoplastic elastomer reinforced with 30% long carbon fiber, offering a superior balance of strength, stiffness, and flexibility. The long fiber reinforcement significantly improves tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for semi structural applications that demand both durability and controlled elasticity—such as automotive components, industrial isolators, robotic joints, and protective gear housings.
- Model number: TPU-LCF-BCA3
- Matrix Resin: Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU)
- Reinforcing Filler: Carbon fiber
- Appearance: Granules
- Grade: Injection/extrusion grade
- Packaging: 25kgs/bag
TPU-LCF30 | 30% Long Carbon Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastic Polyurethane
TPU-LCF30 is a high-strength, semi-structural thermoplastic elastomer reinforced with 30% long carbon fiber. This advanced composite strikes a compelling balance between mechanical rigidity and elastomeric flexibility, making it well-suited for demanding dynamic applications where durability, fatigue resistance, and dimensional precision are essential.
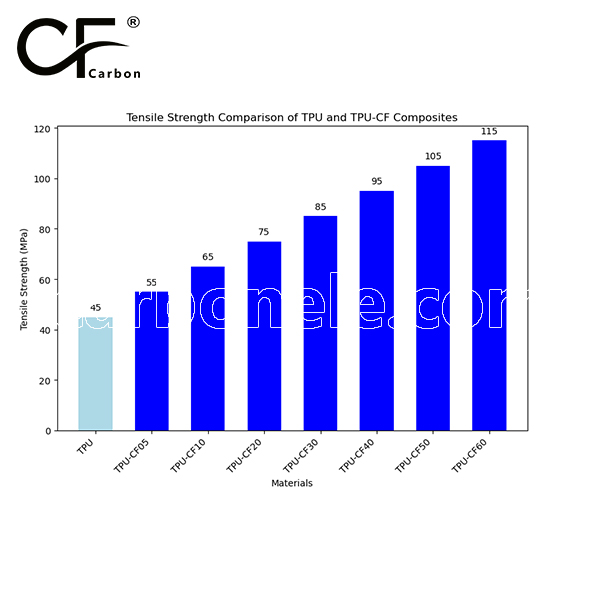
Compared to lower fiber content variants, TPU-LCF30 delivers significantly higher tensile strength, stiffness, and resistance to creep and deformation—while still preserving TPU’s energy return and shock absorbing qualities. The use of long carbon fibers ensures superior load distribution and fatigue life, even under high cycle mechanical motion.
This material is optimized for hybrid components that require lightweight structural performance with controlled flex—ideal for use in automotive subsystems, robotic linkages, industrial isolators, and rugged protection gear exposed to motion, vibration, or impact.
Core Performance Highlights
Mechanical Properties
Carbon Fiber Content: 30% (Long Carbon Fiber, aligned for load path reinforcement)
Tensile Strength: ≥ 70 MPa
Elongation at Break: ≥ 60%
Shore Hardness: ~97A
→ Delivers advanced structural integrity while retaining flexibility for dampening vibrations and impact.
Thermal Resistance
Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT): ~110 °C
Continuous Use Temperature: Up to 100 °C
→ Performs reliably near motors, actuators, or heat generating systems.
Environmental & Chemical Durability
Moisture Absorption: Low — maintains structural performance even in humid or submerged environments
Chemical Resistance: Excellent — withstands oils, fuels, greases, and aggressive solvents
→ Ideal for automotive and industrial settings exposed to fluid or chemical ingress.
Processing & Manufacturing
Molding Methods: Injection molding, extrusion, long fiber 3D filament extrusion
Surface Finish: Matte with noticeable carbon fiber texture depending on mold flow
Tooling Considerations: Use hardened steel tooling and tuned runner design to preserve fiber length and ensure uniform orientation
→ Offers high performance manufacturing with proper tooling adjustments.
Target Applications
Automotive & Mobility
Load bearing brackets, semi flexible mounts, vibration cushioned underhood elements
→ Ideal for replacing heavier PA-CF or metal parts in thermally or chemically exposed zones.
Industrial Equipment
Reinforced joints, wear resistant isolators, structurally flexible machine interfaces
→ Combines mechanical reliability with motion tolerance and reduced maintenance cycles.
Robotics & Automation
Mid load flex arms, rigid flex interfaces, end effector structural shells
→ Enables lightweight hybrid designs with both rigidity and impact tolerance.
Wearables & Protection Systems
Exoskeletal frames, flex rigid armor components, repeated impact inserts
→ Excellent for high strength wearable designs in sports, safety, or field gear.
Performance Summary Table
| Property | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Carbon Fiber Content | 30% (Long Carbon Fiber) |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 70 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ≥ 60% |
| Shore Hardness | ~97A |
| Heat Deflection Temp. | ~110 °C |
| Long Term Service Temp. | Up to 100 °C |
| Water Absorption | Low — maintains shape and strength in wet environments |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent — resists oils, fuels, greases, solvents |
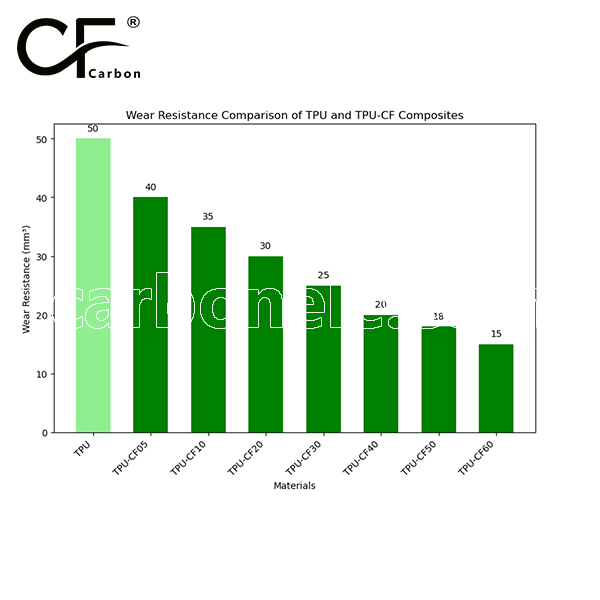
| Wear Resistance | Extremely high — suited for motion and abrasion heavy parts |
| Processing Methods | Injection molding, extrusion, LCF compatible 3D printing |
| Surface Finish | Matte with visible carbon texture depending on fiber alignment |
| Dimensional Stability | High — suitable for flex-rigid components under repeated stress |
Friction coefficient of PA12-LCF
The friction coefficient of TPU is typically between 0.3 and 0.5, while TPU-CF, with added carbon fiber, lowers the friction coefficient to between 0.2 and 0.4. The smaller the value, the better the wear resistance. Therefore, TPU-CF generally offers better wear resistance than pure TPU, especially under high-load conditions.

Frequently Asked Questions
Carbon (Xiamen) New Material Co., Ltd. aims to provide buyers with "one-stop" worry-free high-quality services. Here you can find all information about carbon fiber engineering plastics. If you still have questions, please send us an email for consultation!
-
How can I contact the manufacturer of a product that interests me?
When you find a product you are interested in, you can contact the manufacturer directly by sending an email and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
-
How do I find the products that interest me?
All you need to do is enter the keyword, product name in the search window and press the Enter key on your keyboard. Your search results page will then be displayed. You can also search within the product category pages on the home page. Each category is divided into subcategories, allowing you to refine your search and find products that interest you.
-
Where will I find a buying guide?
Please contact our after-sales service directly and we will provide you with a comprehensive operating guide.
-
What are CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites are materials where carbon fibers are incorporated into a thermoplastic matrix. They combine the strength and stiffness of carbon fibers with the processability and recyclability of thermoplastics. For instance, they are used in automotive parts like bumper beams.
-
What are the benefits of CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites over traditional composites?
The key benefits include faster production cycles, easier recyclability, and better impact resistance. They also offer design flexibility. An example is in the manufacturing of consumer electronics casings where complex shapes can be achieved more easily.
-
How are CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites processed?
Common processing methods include injection molding, extrusion, and compression molding. Injection molding is widely used for mass production. For example, in the production of small components for the medical industry.
-
What industries use CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
They are utilized in aerospace, automotive, medical, and sports equipment industries. In aerospace, they can be found in interior components. In the medical field, they might be used in prosthetics.
-
How does the carbon fiber content affect the properties of the composites?
Higher carbon fiber content generally leads to increased strength and stiffness but may reduce ductility. A moderate content is often balanced for specific applications. For example, a higher content might be preferred in structural parts of a race car.
-
What are the challenges in using CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
Challenges include higher material costs, complex processing equipment requirements, and ensuring uniform fiber dispersion. Issues with adhesion between the fibers and the matrix can also arise. An example is in achieving consistent quality in large-scale production.