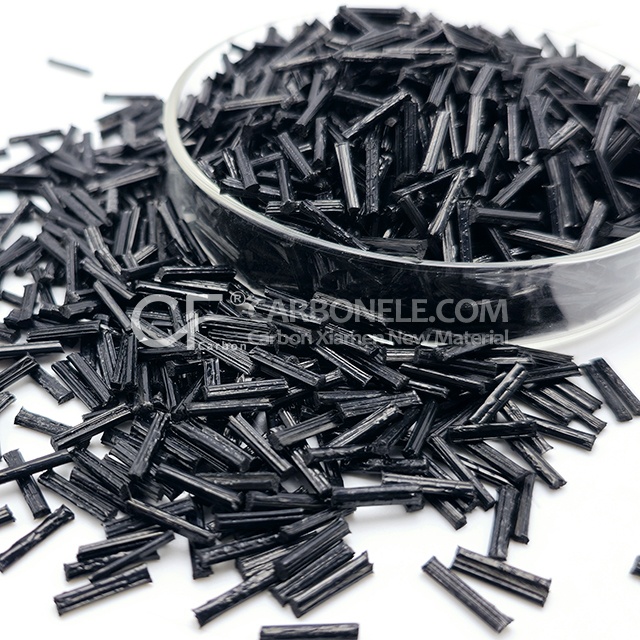
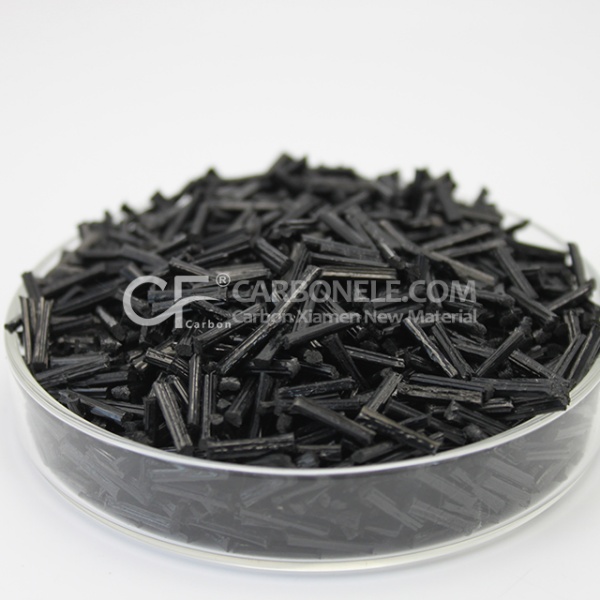
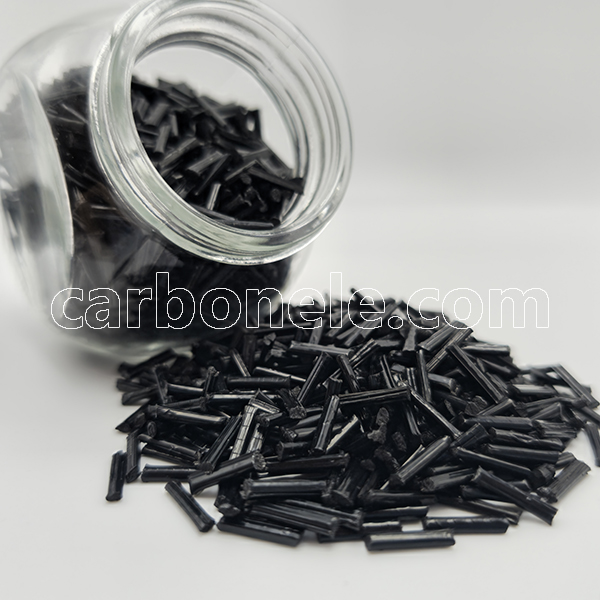
TPU-LCF50 Lightweight Belts for Smooth Conveying
Engineered for precision conveying, the TPU-LCF50 long carbon fiber reinforced belt delivers ultra-light weight, exceptional abrasion resistance and anti-static properties
- Model number: TPU-LCF-BCA5
- Matrix Resin: Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU)
- Reinforcing Filler: Carbon fiber
- Appearance: Granules
- Grade: Injection/extrusion grade
- Packaging: 25kgs/bag
TPU-LCF50 Lightweight Belts for Smooth Conveying
TPU-LCF50 Material Innovation: Strength Meets Flexibility
Thermoplastic polyurethane reinforced with 50% long carbon fibers defines the core of TPU-LCF50. This engineering composite merges polymer flexibility with fiber-enhanced rigidity, creating a unique balance ideal for high-stress dynamic applications. Unlike conventional rubber or short-fiber belts, TPU-LCF50 maintains consistent performance under continuous operation while resisting deformation. The long fibers align along stress paths, distributing loads uniformly to prevent localized wear—a critical advantage for conveying systems demanding precision and longevity.
Why TPU-LCF50 Belts Outperform Traditional Solutions
Ultra-Lightweight Efficiency
TPU-LCF50 belts slash energy consumption by reducing drive motor load. Their lightweight nature minimizes inertia during start-stop cycles, enabling smoother acceleration and deceleration in automated lines. This translates to lower operational costs and extended machinery life.
Unmatched Wear Resistance
Carbon fibers embedded in the TPU-LCF50 matrix create a self-reinforcing surface that resists abrasion from sharp or coarse materials. This inherent toughness eliminates premature belt degradation in industries like recycling or mining, where particulate contact is unavoidable.
Quiet, Friction-Optimized Operation
The low-friction surface of TPU-LCF50 belts ensures silent material transfer—essential in noise-sensitive environments like packaging facilities. Reduced sliding resistance also prevents material spillage during inclined conveying.
Chemical & Moisture Immunity
From food processing oils to industrial solvents, TPU-LCF50 retains integrity where rubber belts swell or crack. Its non-porous structure repels water ingress, preventing bacterial growth in hygienic settings.
TPU-LCF50 in Action: Precision Packaging Conveying
The Challenge: Fragile Item Handling
A premium cosmetics manufacturer faced recurring losses: glass perfume bottles jammed or toppled on standard belts during high-speed filling. Vibration-induced misalignment caused labeling errors, while belt abrasion generated contaminating particles.
TPU-LCF50 Belt Integration
Replacing rubber belts with TPU-LCF50 solutions transformed their line:
-
Stability: The belt’s anti-static surface eliminated bottle slippage during abrupt stops.
-
Gentleness: Micro-vibration damping protected delicate glass from impact fractures.
-
Cleanliness: The non-shedding TPU-LCF50 material met ISO Class 7 cleanroom standards, removing contamination risks.
-
Maintenance Reduction: 24/7 operation without tension adjustments or lubrication cuts downtime by 40%.
This application exemplifies TPU-LCF50’s role in enhancing throughput while preserving product integrity.
Engineering Behind TPU-LCF50 Belts
Fiber-Matrix Synergy
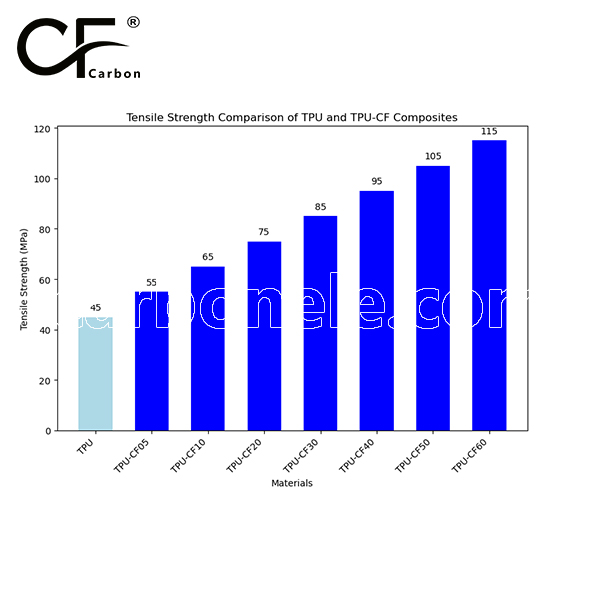
Long carbon fibers in TPU-LCF50 bond molecularly with the polyurethane base. This fusion allows stress transfer from the flexible TPU to the rigid fibers, enabling high load-bearing without brittleness. The result is a belt that flexes around small pulleys yet resists stretching under tons of cargo.
Thermal Stability
TPU-LCF50 maintains dimensional consistency across temperature shifts—from refrigerated logistics to oven-adjacent lines—unlike metals that expand or plastics that creep. This thermal neutrality ensures constant tracking alignment.
Seamless Joint Technology
Welded TPU-LCF50 belt loops avoid metal fasteners that snag products. Fusion joints replicate the belt’s native strength, creating endless surfaces free from weak points.
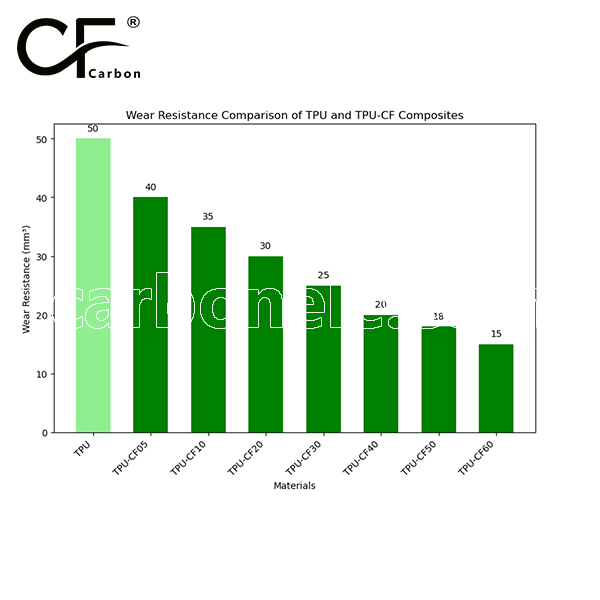
Friction coefficient of PA12-LCF
The friction coefficient of TPU is typically between 0.3 and 0.5, while TPU-CF, with added carbon fiber, lowers the friction coefficient to between 0.2 and 0.4. The smaller the value, the better the wear resistance. Therefore, TPU-CF generally offers better wear resistance than pure TPU, especially under high-load conditions.

Frequently Asked Questions
Carbon (Xiamen) New Material Co., Ltd. aims to provide buyers with "one-stop" worry-free high-quality services. Here you can find all information about carbon fiber engineering plastics. If you still have questions, please send us an email for consultation!
-
How can I contact the manufacturer of a product that interests me?
When you find a product you are interested in, you can contact the manufacturer directly by sending an email and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
-
How do I find the products that interest me?
All you need to do is enter the keyword, product name in the search window and press the Enter key on your keyboard. Your search results page will then be displayed. You can also search within the product category pages on the home page. Each category is divided into subcategories, allowing you to refine your search and find products that interest you.
-
Where will I find a buying guide?
Please contact our after-sales service directly and we will provide you with a comprehensive operating guide.
-
What are CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites are materials where carbon fibers are incorporated into a thermoplastic matrix. They combine the strength and stiffness of carbon fibers with the processability and recyclability of thermoplastics. For instance, they are used in automotive parts like bumper beams.
-
What are the benefits of CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites over traditional composites?
The key benefits include faster production cycles, easier recyclability, and better impact resistance. They also offer design flexibility. An example is in the manufacturing of consumer electronics casings where complex shapes can be achieved more easily.
-
How are CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites processed?
Common processing methods include injection molding, extrusion, and compression molding. Injection molding is widely used for mass production. For example, in the production of small components for the medical industry.
-
What industries use CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
They are utilized in aerospace, automotive, medical, and sports equipment industries. In aerospace, they can be found in interior components. In the medical field, they might be used in prosthetics.
-
How does the carbon fiber content affect the properties of the composites?
Higher carbon fiber content generally leads to increased strength and stiffness but may reduce ductility. A moderate content is often balanced for specific applications. For example, a higher content might be preferred in structural parts of a race car.
-
What are the challenges in using CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
Challenges include higher material costs, complex processing equipment requirements, and ensuring uniform fiber dispersion. Issues with adhesion between the fibers and the matrix can also arise. An example is in achieving consistent quality in large-scale production.